|
五,电路原理图 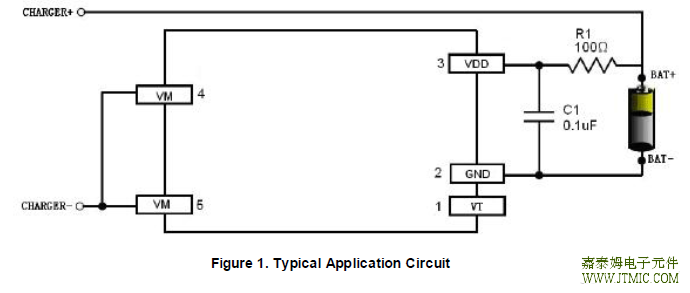 六.产品PDF文档
七,功能概述 Normal operating mode If no exception condition is detected, charging and discharging can be carried out freely. This condition is called the normal operating mode. Overcharge Condition When the battery voltage becomes higher than the overcharge detection voltage (VCU) during charging under normal condition and the state continues for the overcharge detection delay time (tCU) or longer, the JTM5453T turns the charging control FET off to stop charging. This condition is called the overcharge condition. The overcharge condition is released in the following two cases: 1, When the battery voltage drops below the overcharge release voltage (VCL), the JTM5453T turns the charging control FET on and returns to the normal condition. 2, When a load is connected and discharging starts, the JTM5453T turns the charging control FET on and returns to the normal condition. The release mechanism is as follows: the discharging current flows through an internal parasitic diode of the charging FET immediately after a load is connected and discharging starts, and the VM pin voltage increases about 0.7 V (forward voltage of the diode) from the GND pin voltage momentarily. The JTM5453T detects this voltage and releases the overcharge condition. Consequently, in the case that the battery voltage is equal to or lower than the overcharge detection voltage (VCU), the JTM5453Treturns to the normal condition immediately, but in the case the battery voltage is higher than the overcharge detection voltage (VCU),the chip does not return to the normal condition until the battery voltage drops below the overcharge detection voltage (VCU) even if the load is connected. In addition, if the VM pin voltage is equal to or lower than the overcurrent 1 detection voltage when a load is connected and discharging starts, the chip does not return to the normal condition. Remark If the battery is charged to a voltage higher than the overcharge detection voltage (VCU) and the battery voltage does not drops below the overcharge detection voltage (VCU) even when a heavy load, which causes an overcurrent, is connected, the overcurrent 1 and overcurrent 2 do not work until the battery voltage drops below the overcharge detection voltage (VCU). Since an actual battery has, however, an internal impedance of several dozens of mΩ , and the battery voltage drops immediately after a heavy load which causes an overcurrent is battery voltage. Overdischarge Condition When the battery voltage drops below the overdischarge detection voltage (VDL) during discharging under normal condition and it continues for the overdischarge detection delay time (tDL) or longer, the JTM5453T turns the discharging control FET off and stops discharging. This condition is called overdischarge condition. After the discharging control FET is turned off, the VM pin is pulled up by the RVMD resistor between VM and VDD in JTM5453T. Meanwhile when VM is bigger than 1.5 V (typ.) (the load short-circuiting detection voltage), the current of the chip is reduced to the power-down current (IPDN). This condition is called power-down condition. The VM and VDD pins are shorted by the RVMD resistor in the IC under the overdischarge and power-down conditions. The power-down condition is released when a charger is connected and the potential 八,相关产品
(责任编辑:oumao18) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||



